With worldwide efforts being made to curb greenhouse gas emissions, tackling the climate crisis is a top priority for researchers working on low-carbon solutions. Every day at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, MA, students and professors across disciplines work together to advance these goals—testing alternative fuels, modeling renewable energy markets, and experimenting with new forms of energy storage.
“We are in the midst of a reinvention of how we make energy and how we use energy,” says Susan Hockfield, founder of the MIT Energy Initiative. “And we will develop sustainable energy practices for a larger population, a wealthier population, and a healthier planet.”
We asked MITEI Director Robert C. Armstrong to share his thoughts on some of the most significant research impacts the MIT energy community has made over the last 10 years, and what he finds most exciting for the future. Here are the biggest renewable energy developments to come out of MIT over the last decade – and what’s coming for the next.
Looking Back...
Flexible, thin-film solar photovoltaics that can be printed on nearly any surface.

Khethworks, a spinoff from the Tata Center for Technology and Design that is working on affordable solar-powered irrigation for the developing world—allowing customers to farm year-round.
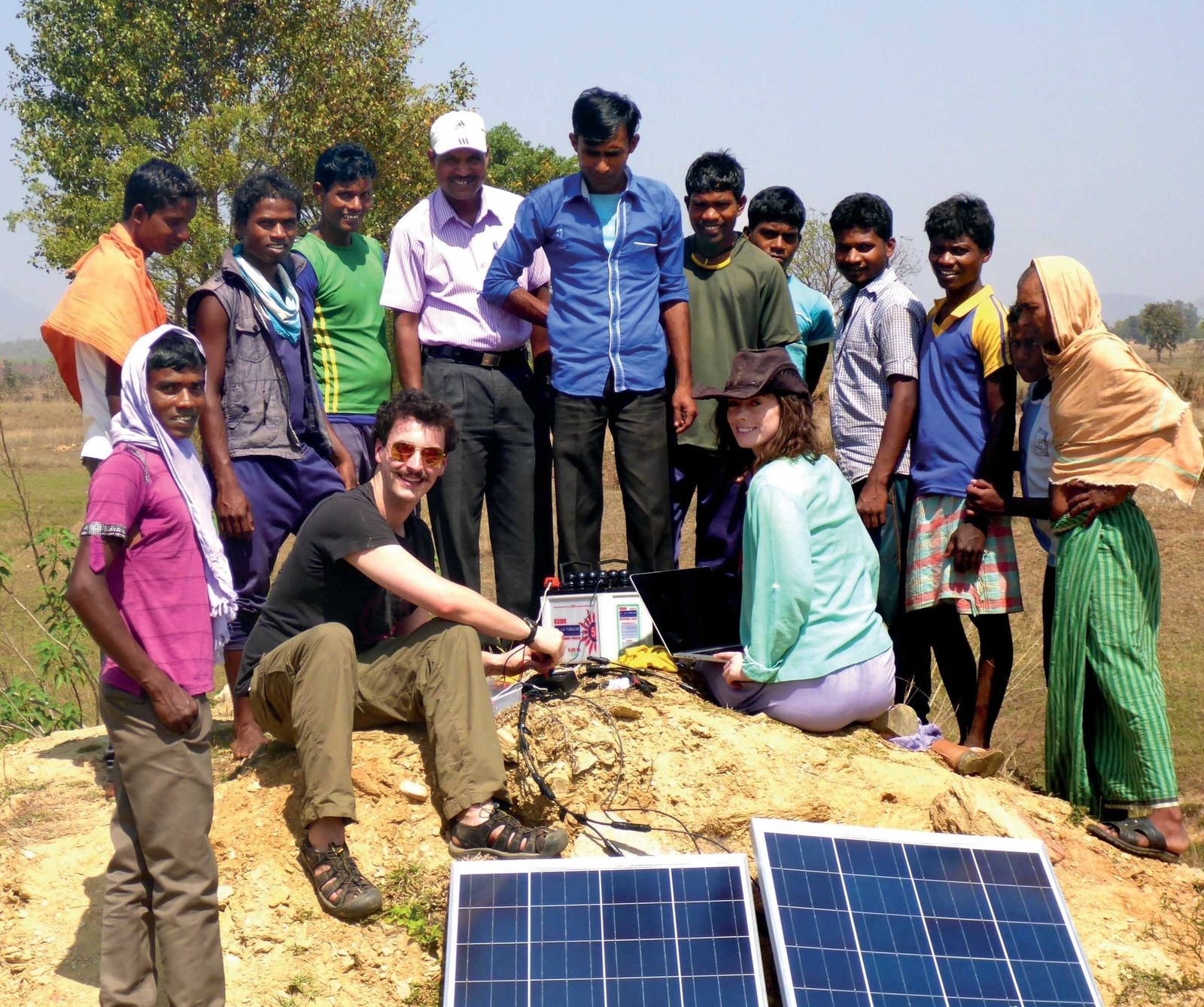

A solar-powered electrodialysis desalination system, which will provide clean drinking water to rural, off-grid villages in India.

Energy storage technologies like 24M, Baseload Renewables, Ambri, and Fast CAP Systems, based on groundbreaking technologies.

Keystone Tower Systems, a company making larger and more efficient wind towers by creating turbine towers on location.

LiquiGlide and Dropwise, two start-ups based on Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Kripa Varanasi's research on engineering super-slippery surfaces.
The tokamak fusion research reactor, which set a record for plasma pressure and paves the way for future nuclear fusion reactors.

Multidisciplinary studies like "The Future of Solar Energy" and "Utility of the Future."

Looking Ahead...
Next-generation solar technologies that lower manufacturing and system integration costs.

Long-term energy storage technologies to enable large-scale wind and solar deployment.

Design and implementation of more robust electric grids for developing and developed nations.

Energy- and climate-conscious urban planning to reduce the energy needs of new cities and neighborhoods, helping to combat climate change and increase resilience while making communities more livable.

Research into how transportation will evolve with developments in technology, fuel, infrastructure, policy, and consumer preference.

New approaches to fusion that are beginning to materialize, such as the small-scale reactor currently being designed at MIT.

Advanced nanoscale materials engineered for high performance in devices.

Student and alumni research, technology, and policy development.


