The Blue Planet gets Blue-er
In June 2014 geophysicist Steve Jacobsen of Northwestern University and Seismologist Brandon Schmandt from the University of New Mexico, along with a team of scientists from across the country, published an article titled "Dehydration Melting at the Top of the Lower Mantle" in Science. Sounds boring, right? Well, if you dig "beneath the surface" it's actually pretty cool and here's why!
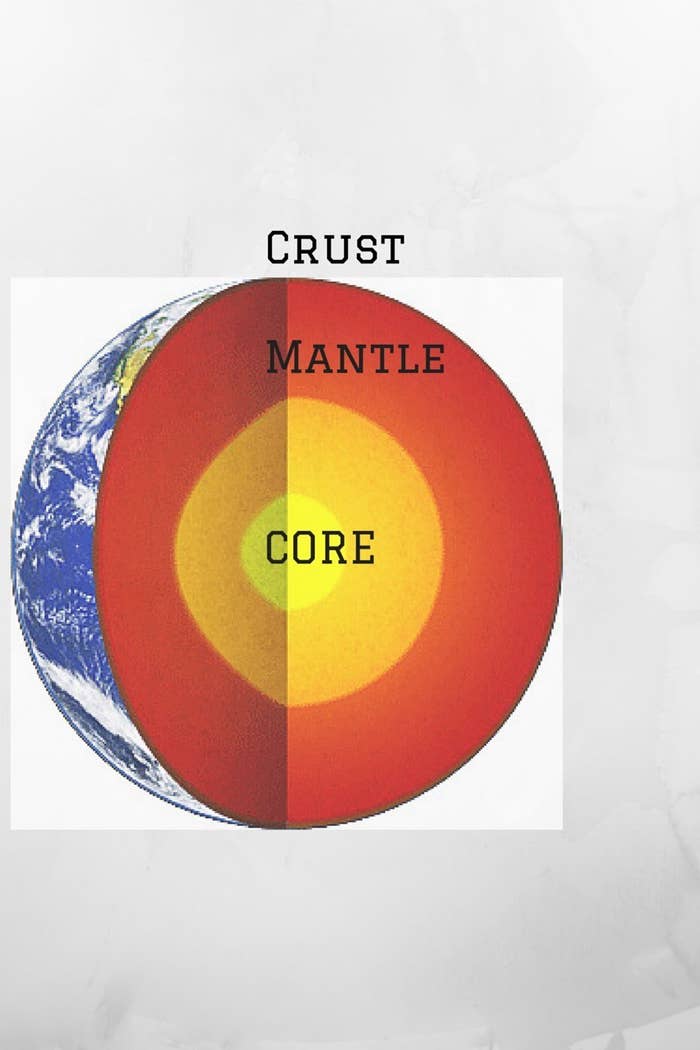
Before we dive in we should quickly refresh your elementary Earth Science knowledge. Let's review the 3 basic layers of Earth. They are: The Crust, The Mantle, and The Core. Easy Right? We sit atop the thin and crumbly crust just above the mantle, a layer of hot, dense, semisolid rock. Yet, like most things, it never is that simple. The mantle is actually made up of its own layers or "zones". As we move down towards the core we encounter the lithosphere, asthenosphere, upper mantle, and lower mantle. Each one of these zones has its own unique and exciting characteristics, but that is an article for another day. What we are concerned with right now is what is referred to as the "transition zone", the area between the upper and lower mantles.
The Layers of the Earth
What these scientists have discovered is a massive reservoir of water potentially containing enough liquid to refill our Earth's oceans three times over. This "ocean" is buried deep within the transition zone below North America, which lies at a depth of 410-660 kilometers below the crust. For us Americans, that is about 255-410 miles. To give you a bit of perspective, the deepest human borehole ever drilled reached only 12km (7.5 miles) before the drill bits began to melt due to geothermic temperatures and extreme pressure. In fact, if you wanted to reach this underground water world by car, you would need to cruise at a constant speed of 70mph for nearly six hours to begin to reach these depths.

Now, it is not exactly the giant pocket of water you may be imagining. The extreme temperatures and immense pressure at these depths actually cause the molecules in the water to split creating hydroxyl radical (OH). What the scientists have found is that at high pressures a mineral called ringwoodite has been trapping water within itself by molecularly combining with the OH, acting like a giant sponge. However, as convection, a natural Earth process, pushes the ringwoodite deeper in the mantle it continues to encounter ever increasing pressures. Eventually, under these forces something has to give and the water begins to squeeze out of the rock partially melting it. This process is called dehydration melting. This expelled "water" is what becomes trapped creating the reservoirs.
Understanding Ringwoodite and Water Reservoirs

The water was discovered through data collected by over 2,000 seismometers across the United States. Although scientists are quick to point out that currently the reservoir has only been detected under North America, the discovery could still have a huge impact on our way of thinking. Perhaps most interestingly, it lends credence to the proposed "Whole-Earth Water Cycle".

Have you ever stopped and thought about where all the water on Earth actually came from? Scientists sure have, and up to this point have not been able to supply a verified answer. Until now, the best guess was the water was deposited from icy comets striking the Earth millions of years ago, melting on impact and depositing what is now our oceans. It seems like science fiction, but if this theory holds true, it may also support our search for extraterrestrial life. Perhaps the organisms that eventually evolved out of the oceans into humans arrived on these comets from outer space. However, with the discovery of underground reservoirs it is possible our origins and our water have both been on Earth since the beginning. This new discovery suggests that water has been slowly seeping out of the mantle filling our oceans over thousands of years, more or less like a leaking hose. The theory of the Whole-Earth Water Cycle also explains why our oceans have not changed size or volume for as long as we know.
If anything, this is just another subtle reminder of how precariously balanced our world is. If these oceans of water were not trapped underground by the pressures of physics and our very precise history, but rather were on the surface of the Earth, the only thing our space traveling friends would ever see were the tops of mountains poking out of one giant body of water.
Think About That!


